A Ride-Hailing Paper Published in Transport Policy
Posted on 1 November 2025 by Songzi ZHOU
Our research group is pleased to announce that the research paper “A spatial agent-based approach to simulating the ride-hailing system and its environmental impacts” has been published in Transport Policy in October 2025! Please click here to read the full paper.
This study developed a spatial agent-based ride-hailing diffusion model with integrated supply–demand dynamics to simulate the interactions among service providers, drivers, and users in Shenzhen, China, from 2023 to 2038 under various future scenarios, and to assess the corresponding environmental impacts.
Key findings include:
- Assuming the market continues to evolve as in the past from 2023 to 2038, the existing market is projected to experience a 36% increase in annual ride-hailing usage, a 24.63% decrease in the average ride-hailing price, and a 73.16% increase in drivers’ compensation.
- Price and compensation affect the ride-hailing system in the early stages and further its carbon emission reduction potential.
- High commission rates can deter both drivers and consumers, reducing the effectiveness of ride-hailing in cutting carbon emissions.
- Carbon emissions reduced by replacing different transport modes by ride-hailing vary.
This research provides valuable insights for urban policymakers to intervene in ride-hailing systems.
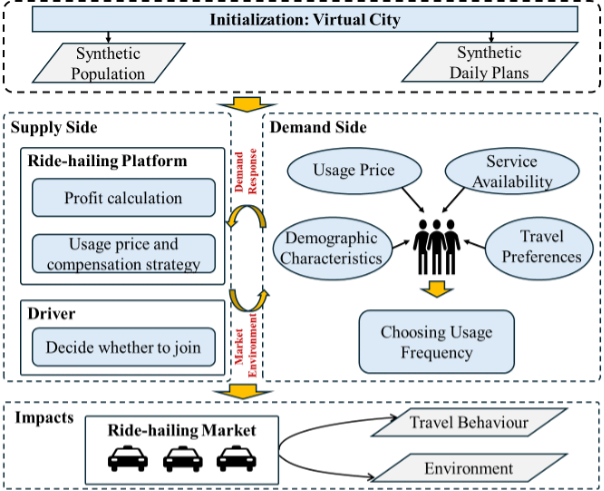
Conceptual Framework for Analyzing the Impact of Ride-Hailing on Travel Behavior and Environment
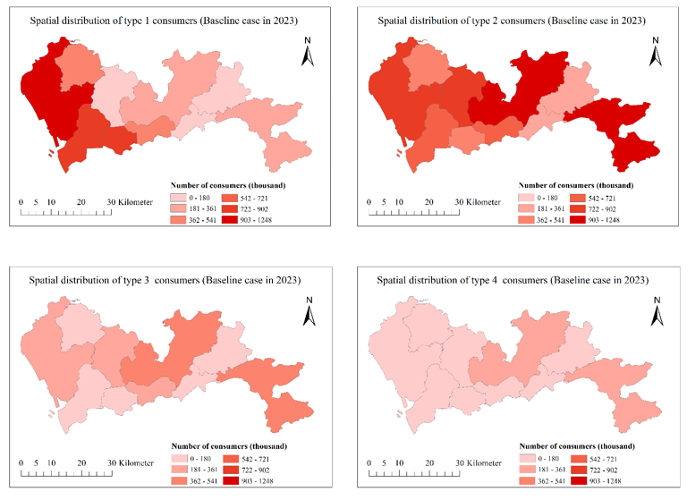
Spatial distribution of four types of consumers in 2023 in the baseline Shenzhen scenario
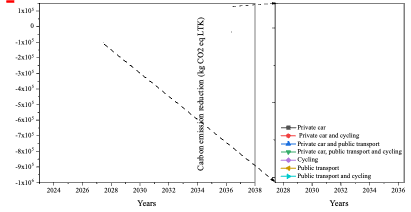
Carbon emission reduction under different transport modes in the Transport Scenarios
